Highlight

Successful together – our valantic Team.
Meet the people who bring passion and accountability to driving success at valantic.
Get to know usAugust 29, 2025

It’s been a while since our last blog post in June. Since then, there have been several wave deployments with exciting innovations and useful customizations. We will present what we believe are the most important updates here now that the summer break is over. This time, the focus is on data modeling and data integration, with new connections to SAP Datasphere. But there are also some interesting new functions and adaptations to the data catalog and administration.
In addition to options for data modeling processing, correctness also plays a crucial role in achieving a meaningful model. That’s why data validation of hierarchies has been expanded. Validation now includes a check for missing hierarchy nodes. Each hierarchy defined in the hierarchy with directory must provide nodes for all corresponding third-party key values used in fact records. This means, for example, if records in fact have the currency key “USD” but it does not exist as a hierarchy node, all data assigned to “USD” will not exist in the aggregation under the hierarchy. These missing nodes can now be identified and exported. You can then manually update them or summarize all missing nodes under the “MISSING” node to avoid losing the data in the view.
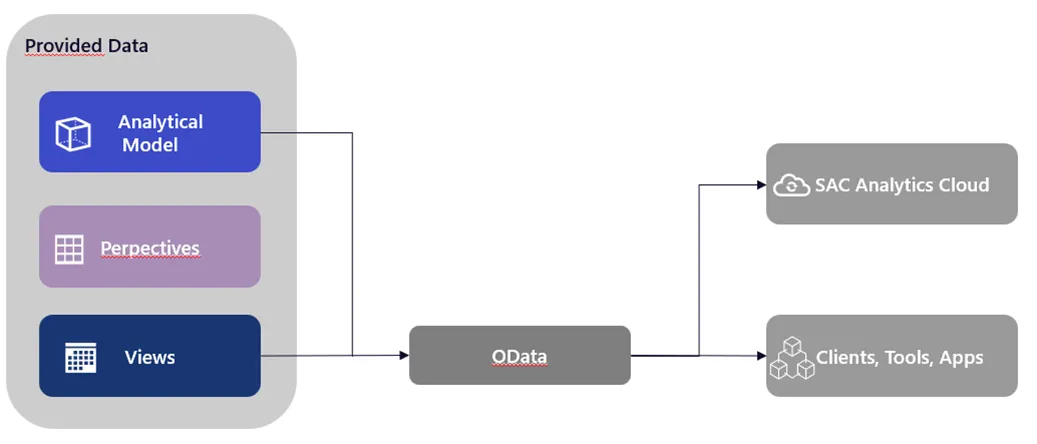
The creation of OData service routes has been simplified significantly for assets in data modeling since it is now possible to generate an OData request. For example, if you have just created a new analytical model, you can send this version directly to another user by generating it. This allows easy splitting of objects to test them directly in SAP SAC, for example.
In addition to generating OData service routes, the $batch syntax has been introduced for the OData consumption API because data consumers such as SAP Build and SAP Fiora Elements apps can only be used with the $batch OData syntax. Note that the content of the text of a $batch request is limited to a single GET request. This is how SAP shows that it is constantly working on better linking its own products on different levels.
Among the recent innovations, derived variables on filter variables and variables for restricted KPIs have been made available, which allows these variable types to profit from the advantages of derived variables. The value of the variable is retrieved from the system via a lookup entity. A tangible example is a country/currency dependency. If a country is specified, the currency can be determined automatically. Other advantages include the ability to reuse lookup entities in several analysis models and central data maintenance.
With regard to data modeling, SAP continues to optimize the object database. Incremental aggregation can now be selected for the transformation flows in the object storage file memory. If the data loads are already incremental, aggregated results can be maintained efficiently. There is no need to wait for the entire load or analyze the whole local table (file).
There is also an adjustment of the transformation flows. The drag-and-drop function is now available in the file memory, so it will be familiar to users of SAP Datasphere. The handling of data processing in the object storage and in classic SAP Datasphere spaces is thus standardized, which makes it easier to get started and use.
The data types for local tables (file) in the object store have also been extended to include DateTime, hana.BINARY, and HANA.TINYINT. These can then be used for data modeling and partitioning, which is a welcome extension of the object storage, especially with DateTime.
See the additional note at the end of this blog post for those who prefer Python or SQL scripting over graphical views. The editor in SQL Views now displays syntax errors in SQL sources in the message area marked with line numbers, or it highlights the incorrect lines. Corrections in the right place can be made faster, which ensures a better workflow. With Python, version 3.11 is now available, and 3.9 has been discontinued.
A large number of different source systems with configuration options are crucial for flexible and comprehensive data integration. Accordingly, this section of our blog post is about the replication flow and its latest updates.
With these innovations, it is possible to integrate a SQL or script view directly into a replication flow as a source. The SQL and Script View as source is available for SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA On-Premise, and SAP Datasphere. There are restrictions on usage because only the load type “Only Initial” can be used; the view must not contain any parameters, and a primary key must be defined. This new feature provides direct access without further processing steps, which simplifies development and the testing of new ideas.
In our last blog post, we reported on SFTP as a new way to integrate data into SAP Datasphere. Since these changes, SFTP has been available as a source for replication flows. As with SFTP as a direct source, the “Only Initial” load type is the only option in a replication flow. Source settings let you adjust performance and features to suit your needs. For example, the maximum number of partitions allows you to determine the resources used to prevent system congestion. The “Include Subfolders” option can load more data because subfolders are traversed recursively. For a detailed overview of the functionalities, SAP has provided an overview here: SFTP and Replication Flow. This shows how SAP is constantly expanding the scenarios in which it provides a native solution to problems. The automated import of CSV files via SFTP does not replace S4/Hana or similar source systems, but it can be a transitional solution until a complete migration is completed or if individual CSV files are required as a basis.
To improve the performance of replication flows, RFC rapid serialization was enabled in the SAP-S/4HANA cloud. This can be an advantage, especially for large amounts of data. Quick serialization is automatically set for newly created replication flows. This must be done manually for existing flows, however.
Another new feature for replication flows is the option to set the load type to “Only Delta.” In certain business cases, the initial data transfer can be omitted. This reduces the memory requirement and also allows you to create tables that allow comparison between initial data and Delta changes.
In addition to the replication flows, task chains have received several updates. We would like to highlight a minor change with which we are very pleased, namely, the new layout option. It is now possible to display task chains from left to right and from top to bottom (default). This is a personal preference that some other users may share.
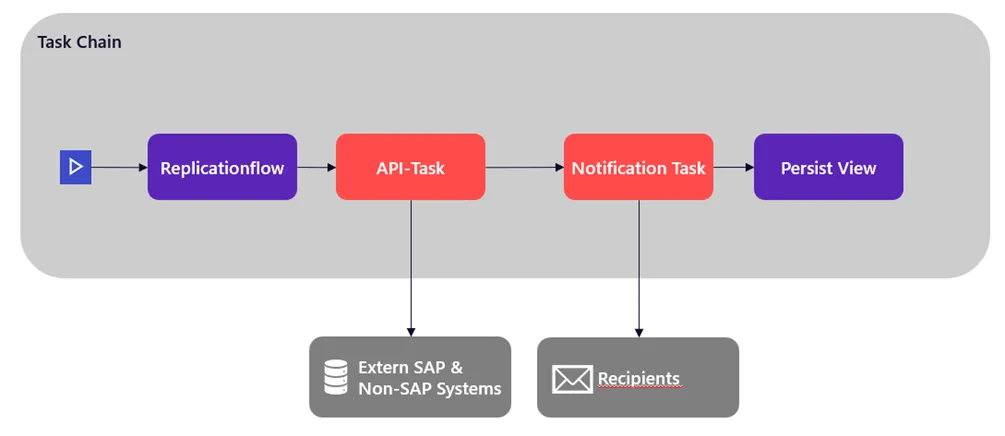
Task chains now also have a new feature: you can access external systems with REST-based API calls. To do this, you must first create a connection of the “Generic HTTP” type. Here you can choose between the authentication types “No Authentication,” “User Name and Password,” or “OAuth2” with client credentials, or username and password. In addition, there are various configuration options, such as whether the system is an on-premises system or a cloud variant, or whether the cloud system has a location or is virtual. The API calls are limited to the POST and GET methods, which establish communication with external systems. For example, this makes it possible to report the status of a specific task chain, to save an intermediate result, or to create a log at an external location. For asynchronous requests, the status can be checked retrospectively using the GET method.
Notification tasks can now be integrated for the task chains. These can be installed at any point, and the corresponding message defined. The recipient list is the same as that of the task chain itself. If an intermediate step fails, the person responsible will receive a specific message directly. Similarly, users who are waiting only for a single item to complete can be notified directly, rather than waiting for the entire task chain to complete.
Regardless of replication flows and task chains, there are other customizations and updates in various areas. For example, the filter options for deleting data were extended to include “Date” and “DateTime.” This allows you to erase erroneous data in a certain period of time or all data up to/after a certain time. It can be used for a wide range of time-stamped scenarios and provides a welcome extension.
There are also some useful new features for the administration of the object database. There are new monitoring features on the Object Storage tab that affect memory consumption in file spaces and the use of Apache Spark applications. This allows you to see where consumption is highest in the file spaces (or SAP HANA data lake files) and how Apache Spark applications work.
As an additional new option in the object store, it is now possible under “Requirements” to define the expected number of API calls per month. This allows API requirements to be defined separately, providing greater control and accuracy in estimating object storage requirements. Together with the new monitoring capabilities, the object store can be analyzed more precisely to achieve a custom-tailored configuration of storage requirements and costs.
There are also other updates for managing the SAP Datasphere tenant. Administrators no longer have to submit tickets to activate SAP HANA for SQL Data Warehousing. Mapping between the SAP Datasphere tenant and the SAP Business Technology Platform account can be done independently. The setup process is more flexible and faster, which reduces SAP wait times and gives administrators more control over their systems.
For SAP Datasphere tenants, there is also the “Activate SAP HANA Multi-Availability Zones” option. It allows you to create a synchronous replica of the main system in a different region on the “Tenant Configuration” page. The synchronous replica has a high-availability setup that can handle processing when needed. The different regions ensure that even in the event of problems in individual zones, the workload can be shared, and all services are available.
The last administrative innovation we would like to present provides the most important advance, in our opinion. It is possible to create an OAuth client with the purpose “Technical user.” This enables use of the SCIM-2.0 API for user and role management, the transport of content via SAP Cloud Transport Management, the export of user activities as CSV, and the use of the Datasphere command line interface currently in the field of “Marketplace” functions. The technical user enables an interaction-free automation of recurring processes and does not require a graphical interface like a browser. Interaction with services, such as in the SAP BTP Cockpit, can thus take place without manual input. One can hope that SAP will continue expanding the technical user’s functionalities in future updates to enable ever better management of the system.
If you are using an SAP BW/4HANA system, it can now be connected directly to the catalog. Various objects can then be included in the catalog, such as AREA (InfoArea), ELEM (BW-Query), IOBJ (InfoObject), and others. A catalog administrator can enrich the objects with terms, KPIs, and tags to publish these for easier searching. The direct connection eliminates the need for integration and processing of objects via other means and enables seamless connection via BW/4HANA systems in order to maintain its catalog efficiently. For specific restrictions on the systems and the objects to be extracted, please consult the SAP documentation: SAP documentation.
For the ELEM objects in your SAP Analytics Cloud story, for data products with SAP Datasphere as the source, and SAP Analytics Cloud insight with a local SAP Datasphere system, an advanced “Impact and Source Analysis” diagram is now available. This allows you to identify dependencies directly and make any necessary changes or insert missing objects.
As data catalog optimizations and new features evolve, it will become easier to use the catalog environment. New features include updated avatars and colors for the grid view on the catalog search page, customized pages for creating and managing the glossary terms and KPIs mentioned, and improvements to metadata extractions. SAP shows that it not only extends the functionality of the data catalog but also improves the user experience. All this makes it easier for users to get started and use the catalog and therefore makes it more attractive.
With the latest changes, SAP offers a wide range of automation tools, via task chains, replication flows, and the “technical user,” requiring fewer manual interventions. The time gained can be used for an optimized analysis of a company’s own models and data products. SAP continuously improves the handling of SAP Datasphere while increasing the added value you get from your data.
The SAP Road Map Explorer provides an overview of upcoming developments. The planned quarterly updates and ideas that continue to shape SAP Datasphere are presented there.
valantic will be pleased to assist you if you need support or have questions regarding SAP Datasphere.
Don't miss a thing.
Subscribe to our latest blog articles.