Highlight

Successful together – our valantic Team.
Meet the people who bring passion and accountability to driving success at valantic.
Get to know usJune 17, 2022

SAP Asset Strategy and Performance Management empowers asset-intensive organizations to define, plan, and monitor optimized maintenance strategies for their physical assets. By delivering relevant data and actionable insights in a clear, structured format, it enables smarter decision-making and drives operational excellence.
In asset-intensive industries, achieving the right balance between maximizing machine output and minimizing operational input is an ongoing challenge. Profitability hinges on the availability, speed, and quality of production – machines must perform reliably at high speeds and deliver consistent results.
At the same time, operational input – especially maintenance costs – needs to stay low. This balance is complex, as output and input are tightly connected: Increasing maintenance can improve availability, performance, and quality, while reducing it may compromise overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
While this relationship generally holds true in principle, the ideal balance between output and input depends on the specific context. Three key factors influence this equilibrium:
Ultimately, companies must weigh both input and output to navigate this delicate balance and drive sustainable performance.
The ISO 55001 standard defines the requirements for effective asset management systems, with a strong emphasis on the ongoing evaluation of cost, risk, and performance. By fostering greater transparency – often absent in traditional maintenance approaches – the standard helps organizations make more informed, strategic decisions.
Many companies struggle to quantify how reduced maintenance affects the likelihood of equipment failure or how increased maintenance can boost availability. Gaining these insights is essential for developing effective maintenance strategies aligned with the DIN EN 13306 standard.
A critical aspect of this process is selecting the right maintenance approach: Is corrective maintenance – where action is taken only after an asset fails – enough to ensure operational efficiency? Or is preventive maintenance, involving scheduled servicing at fixed intervals or based on asset condition, a more effective approach? In many cases, predictive maintenance offers the most strategic advantage. By leveraging real-time machine data and analytics, organizations can forecast potential faults and determine the optimal timing and scope of maintenance activities.
Effectively implementing ISO 55001 requires more than traditional tools – basic Excel spreadsheets are no longer sufficient for managing complex asset data and analytics. Robust, integrated IT solutions are essential for achieving transparency, traceability, and efficiency in asset management.
SAP offers powerful cloud-based solutions through its SAP Intelligent Asset Management Suite, part of SAP Leonardo. These solutions are designed to work seamlessly with SAP Plant Maintenance in both SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA environments.
The suite includes the following:
SAP Asset Strategy and Performance Management provides access to detailed machine and plant data, supporting the development, execution, and monitoring of optimal maintenance strategies. A range of integrated tools guides users through this process.
It all starts with collecting and structuring relevant data to evaluate asset costs, risks, and performance. Data from SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) is transferred to Asset Central in the cloud and standardised according to frameworks like ISO 15926, IEC 60050, ISO 14224, EN 15380, and eCl@ss.
Once the data has been collected, a risk score can be calculated for each asset, reflecting the likelihood and potential impact of failure. This score takes into account multiple factors, including operational context, environmental conditions, and safety implications.
By combining the probability of failure with its potential consequences, the asset’s criticality is determined. This assessment helps gauge how significantly a machine or system failure could affect value creation. Assets identified as highly critical should undergo in-depth analysis.
Potential maintenance strategies:
Based on the conducted analyses, appropriate maintenance strategies are defined, implemented, and carried out for each asset. The resulting data is systematically recorded and consolidated. It forms the foundation for ongoing evaluation and continuous improvement.
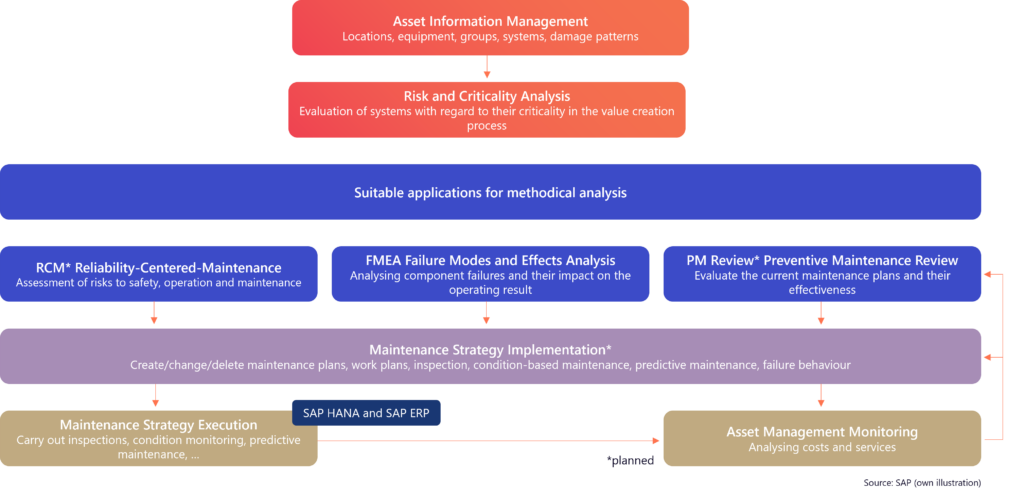
SAP Asset Strategy and Performance Management creates transparency regarding the maintenance costs, failure risks, and performance of each asset. This transparency equips companies with a solid foundation for making informed decisions about the most suitable maintenance strategy – tailored to each individual asset.
One of the key advantages of the solution is its adaptability: Maintenance strategies can be continuously assessed and refined. The platform enables real-time monitoring of asset performance and strategy effectiveness, allowing companies to quickly determine whether implemented measures are delivering the intended outcomes.
Moreover, as external conditions evolve, maintenance strategies can be recalibrated. For instance, cost-efficient sensors may make predictive maintenance viable for assets where it previously wasn’t justified, opening up new opportunities for optimization.

Strategic asset performance management
How to assess the risks of your technical systems and adapt an optimum maintenance strategy accordingly.
Don't miss a thing.
Subscribe to our latest blog articles.