Highlight

Successful together – our valantic Team.
Meet the people who bring passion and accountability to driving success at valantic.
Get to know usAchieving ESG expertise with valantic
valantic provides in-depth insights into the pragmatic fulfillment of ESG reporting and legal requirements, supported by innovative tools and tailored consulting that promote transparency and stakeholder trust.

Legislation Insights: navigating legal requirements in the ESG context

In today’s business world, ESG reporting (Environmental, Social, Governance) is no longer merely an act of goodwill but a legislation-driven, central component of corporate governance that has far-reaching impacts on the entire company. The significantly increased requirements for ESG reporting, driven by a dynamic regulatory environment, are presenting companies with new challenges. Initiatives such as the European Green Deal and related legislation— including the EU Taxonomy, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), the EU Disclosure Regulation (EUDR), and the Act on Corporate Due Diligence in Supply Chains — are increasing the pressure on companies to transparently and comprehensibly present their sustainability performance.
The new CSRD requirements move ESG reporting away from being an optional part of reporting and into the audited annual financial statements. Nevertheless, sustainability plays a driving role in only a very small percentage of companies today. Although some companies define and regularly report sustainability KPIs, only a fraction of these companies have integrated reporting of both financial and non-financial KPIs.

These challenges are relevant not only for compliance reasons but also due to new ESG legislation. They emphasize the importance of transparent and audit-proof reporting processes from both legal and risk management perspectives. Companies must be able to fully document and present their ESG data and practices to prevent legal risks and gain and maintain the trust of investors, customers, and the public. Through the EU Taxonomy, ESG issues become key drivers in investment decisions.
Furthermore, it is crucial for companies to keep an eye on the costs associated with ESG reporting. Potentially labor-intensive and manual reporting processes can lead to significant costs that burden the EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Ensuring low costs through efficient, automated processes is therefore not only a matter of economic viability but also a strategic imperative to protect the financial performance of the company.

Overall, ESG reporting requires a holistic approach and coordinated action from all business areas. It is a complex puzzle that can only be solved if every piece—from procurement and production to distribution and the finance function—contributes its part. Companies that master this challenge and understand and implement ESG as an integral part of their business strategy not only meet regulatory requirements but also position themselves as responsible and future-ready players in the global market.
We show you which levers make your ESG reporting effective and efficient. valantic supports you in the pragmatic implementation of a long-term efficient solution. Thanks to our comprehensive expertise in sustainability, digitalization, and ESG reporting, we are the perfect partners to quickly and optimally implement your requirements. Here, all innovations and adjustments are seamlessly integrated into existing processes and systems to make the integration of ESG reporting as efficient as possible—always within the framework of applicable legislation.
We have repeatedly and successfully demonstrated our expertise in a variety of projects for many satisfied clients. Upon request, we gladly facilitate exchanges with reference clients.
Are you just starting your sustainability transformation? Learn here how to identify the relevant topics for you within the framework of a materiality analysis and how to capture the necessary data points.
The critical aspect of the implementation phase is defining an optimal system landscape for sustainability reporting within your company’s existing architecture. This includes selecting suitable software for ESG reporting. Below you will see an excerpt of the software that we have already successfully implemented in projects. Once we have jointly found the appropriate software support for you, we offer assistance in implementing the reporting requirements, starting from building the data model and reports to interfaces, testing, training, and go-live support.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) also provides valuable support in meeting reporting obligations. By applying AI, companies can simplify data collection and report generation, helping them achieve their ESG goals in a pragmatic and cost-efficient way. Use cases range from automatically extracting data from documents such as energy certificates or invoices, to collecting data from suppliers, to generating reports automatically. In addition, AI models can analyze new ESG legislation updates and translate complex ESG rules and standards—such as the CSRD—into clear, actionable insights for companies.
Data collection
Report generation
Analysis and interpretation of regulatory requirements
Do you have access to multiple software solutions and AI applications or are you unsure which one is best for you? No problem. We guide you in your choice tool-agnostically. As an example, we show you the advantages of ESG reporting with CCH Tagetik, with which we have been intensively collaborating as a long-term partner.




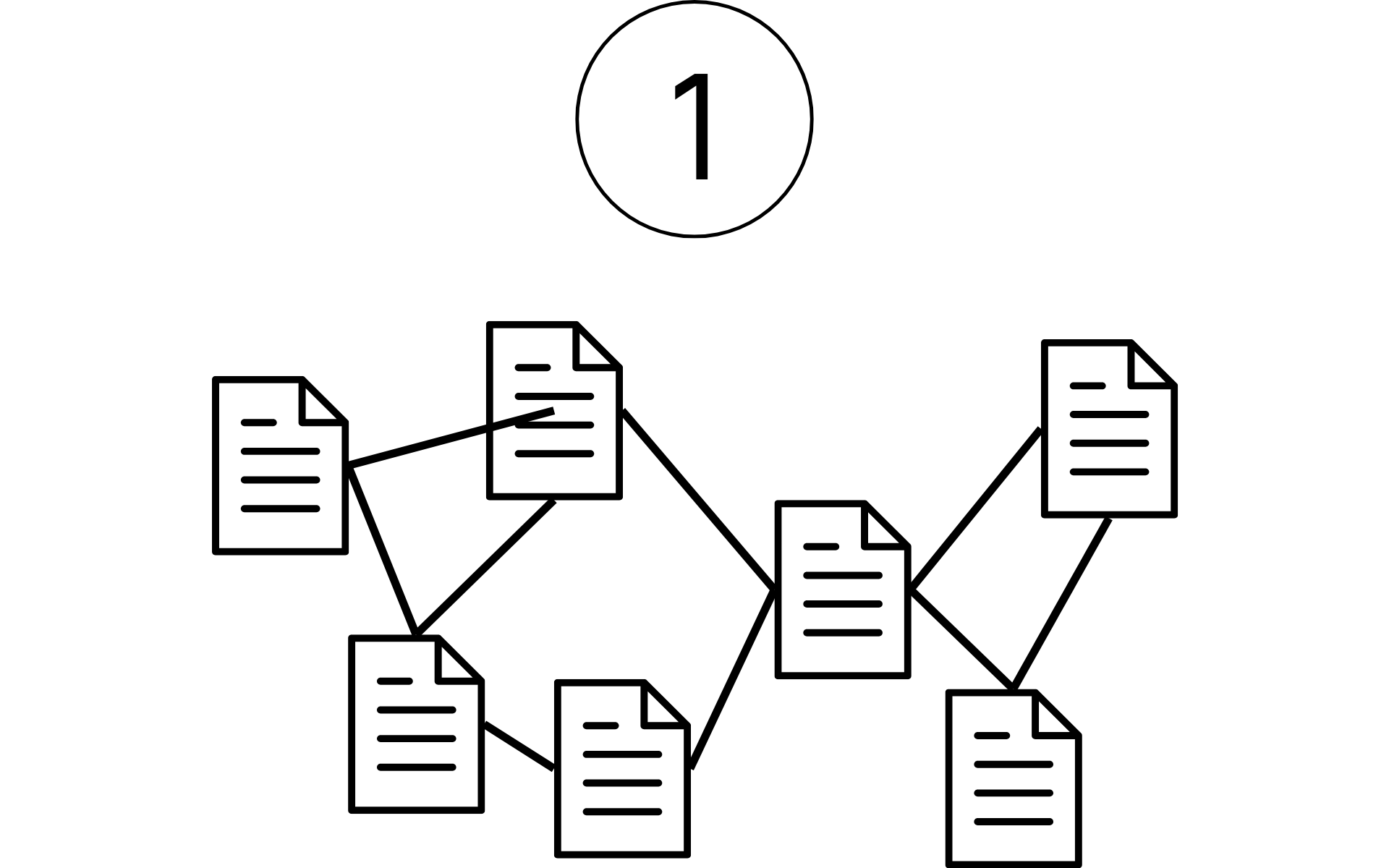
Manual processing
How do we determine the audit-relevant information?
In an Excel-based process, all mandatory information for ESG reporting is compiled.
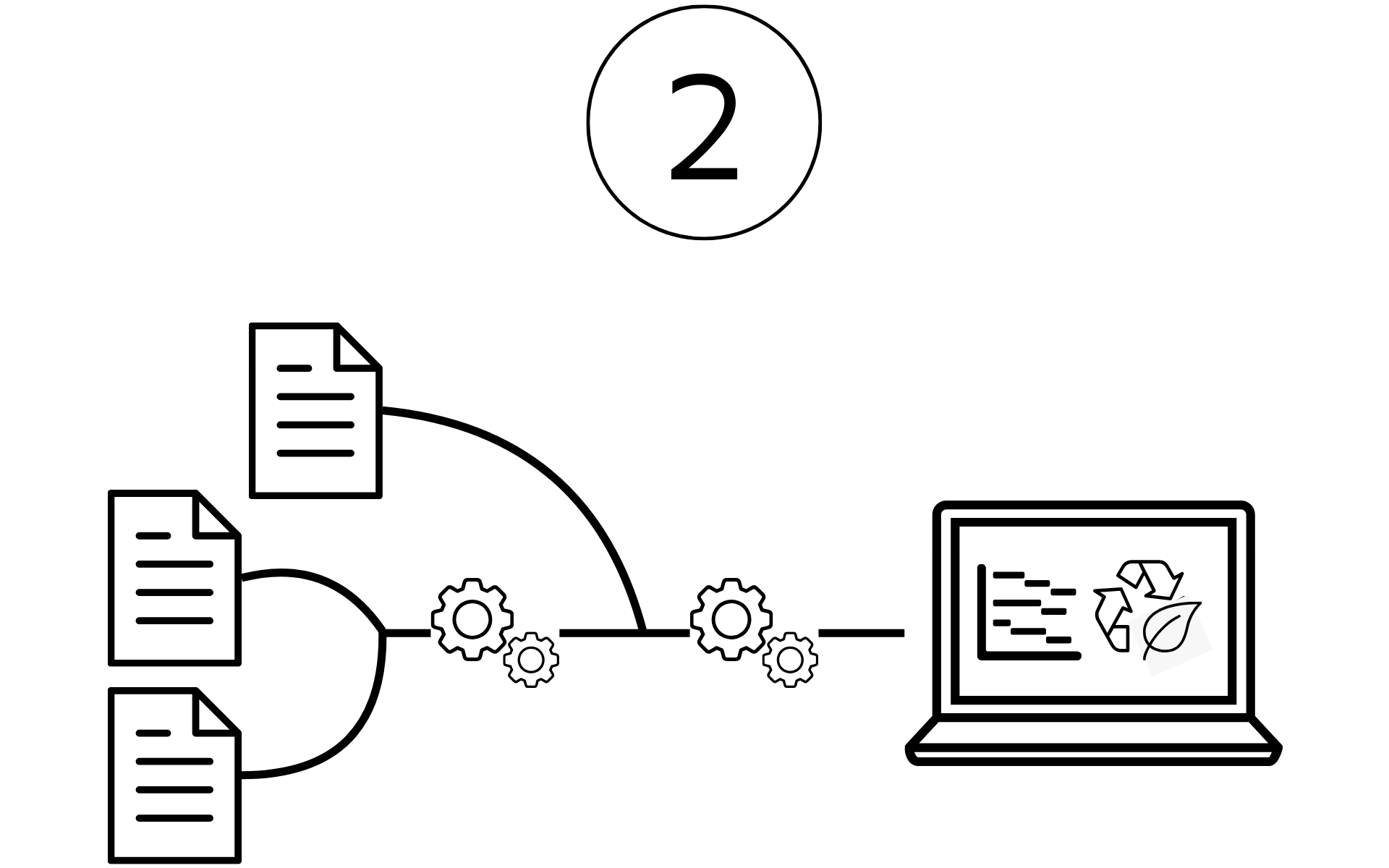
Manual input, structured processing
How can we efficiently process information?
Largely manually captured mandatory information from the respective upstream systems is processed for ESG reporting in a system-supported manner.
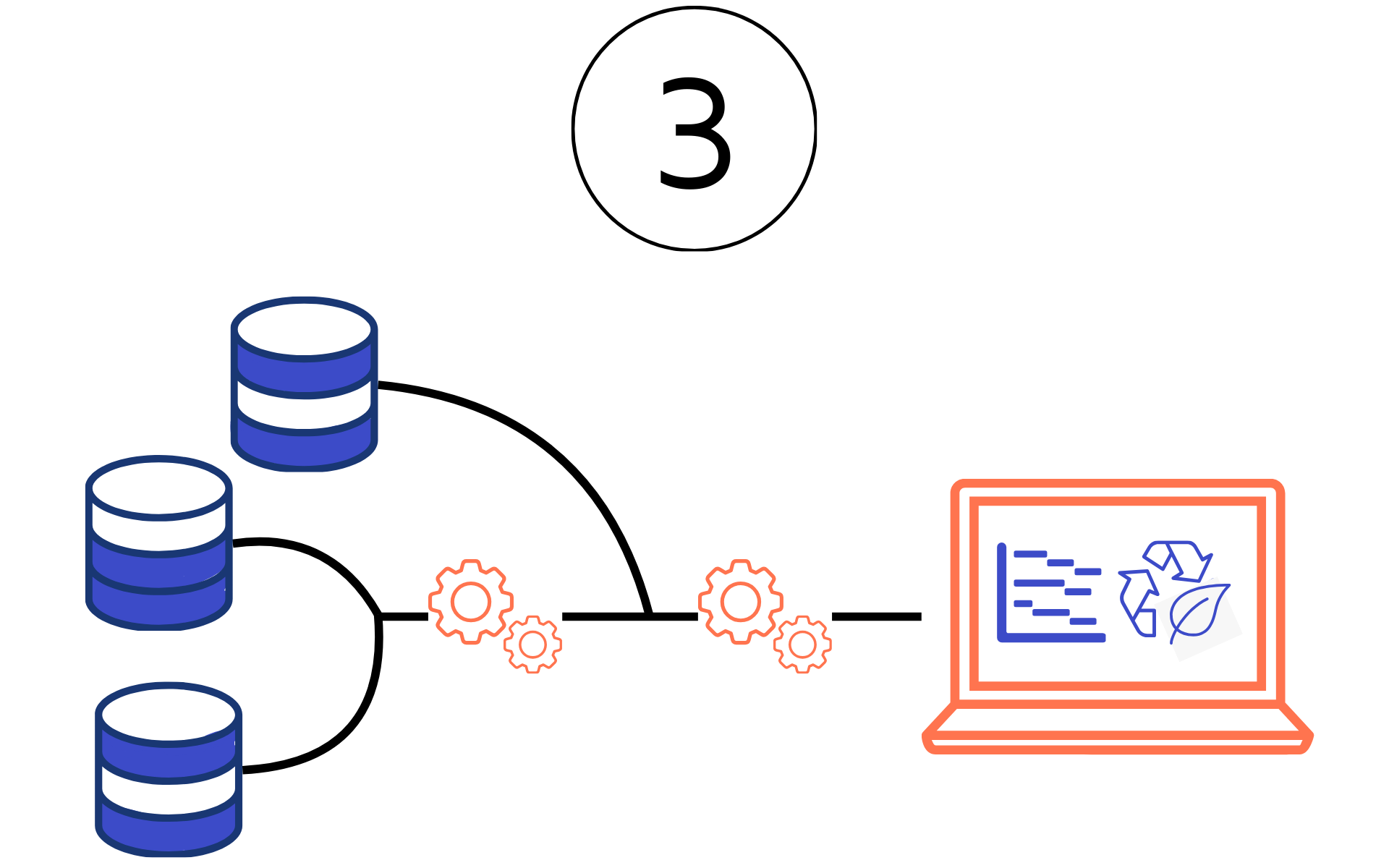
Automated collection, digital processing
How can automated and digitized integration occur?
Mandatory information for ESG reporting is automatically collected from upstream systems and digitally processed all the way to reporting.
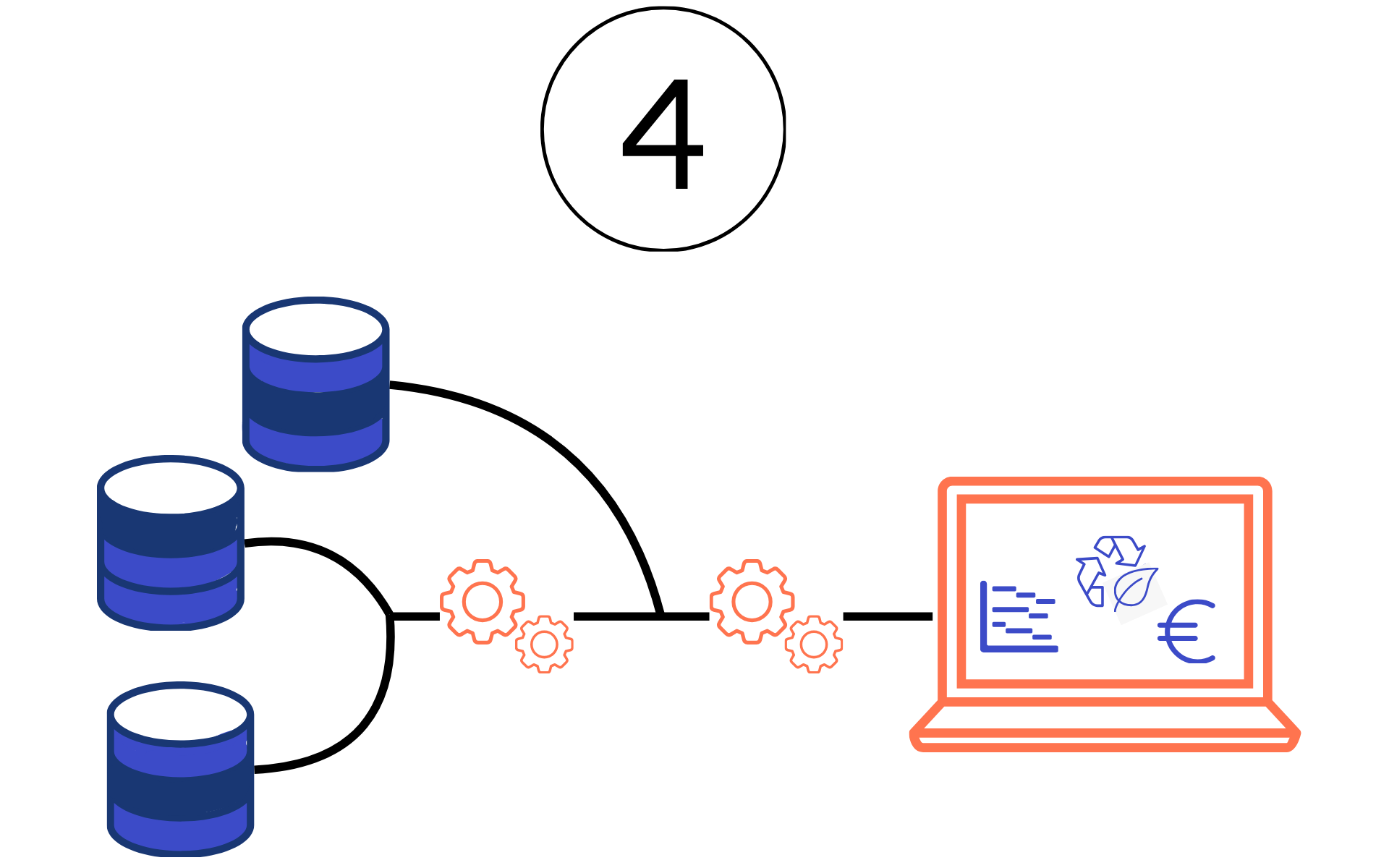
Networking financial & non-financial data
How do we combine non-financial and financial information?
The non-financial information from ESG reporting is combined with data from finance and risk management to make better decisions.
Here's how to efficiently align your financial and non-financial reporting from the start.
Integrating legislative requirements into ESG reporting minimizes legal risks and increases process efficiency.
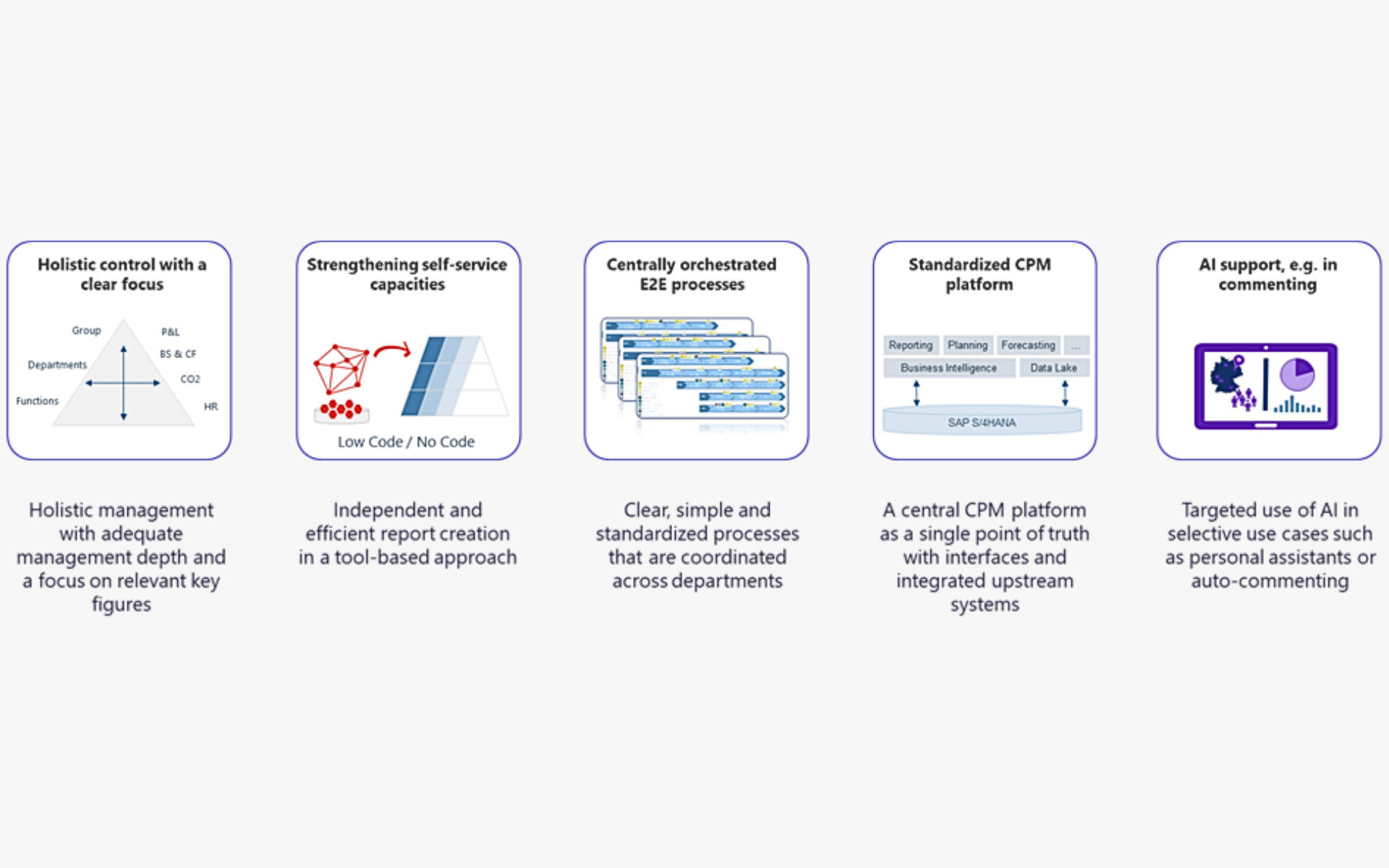
ESG Legislation: levers for efficient reporting
A holistic CPM (Corporate Performance Management) approach reduces complexity and thus costs in processes and systems.
Avoiding manual activities in data preparation conserves valuable resources.
Simulation-capable business cases enable a focus on value-enhancing ESG activities.
Auditable information processing as a success guarantee for audit processes.

Marco Fuhr
Managing Consultant
valantic

Jan Laakmann
Partner
valantic

Dr. Jens Lehnen
Principal
valantic

Sebastian Badaghlou
Partner & Managing Director
valantic