SAP Credit Management in SAP S/4HANA: Recognize Default Risks Early On
March 22, 2022

March 22, 2022

Managing credit risk and recognizing them early is indispensable for successful risk management – and not just since the Corona pandemic. Many companies have long been using credit management as an effective control mechanism to protect themselves proactively from financial loss when making credit decisions. With SAP S/4HANA, SAP has reorganized its solution portfolio in this area (Simplification Item – SAP Note 2270544) and made it available under the name SAP Credit Management.
For companies to take full advantage of SAP Credit Management, they should first form a picture of the changes, features and topics to be considered before embarking on a SAP S/4HANA implementation. The following points in particular should be clarified before the project launch, since they will impact the product scope:
Particularly in the Finance space, SAP S/4HANA has not only implemented fundamental innovations such as the business partner concept and ledger technology, but also optimized the existing applications. This includes the legacy credit management solution, SAP R/3. The classic credit management module (FI-AR-CR) no longer exists under SAP S/4HANA, and its functionalities have been transferred entirely to the FSCM component, which was previously marketed as a separate product.
The new Credit Management component will in future be marketed under the name SAP Credit Management (FIN-FSCM-CR), offering different functional scopes depending on whether the Basic Credit Management or Advanced Credit Management version is implemented. While the former is included license-free in the SAP S/4HANA Standard package, Advanced Credit Management requires an additional license.
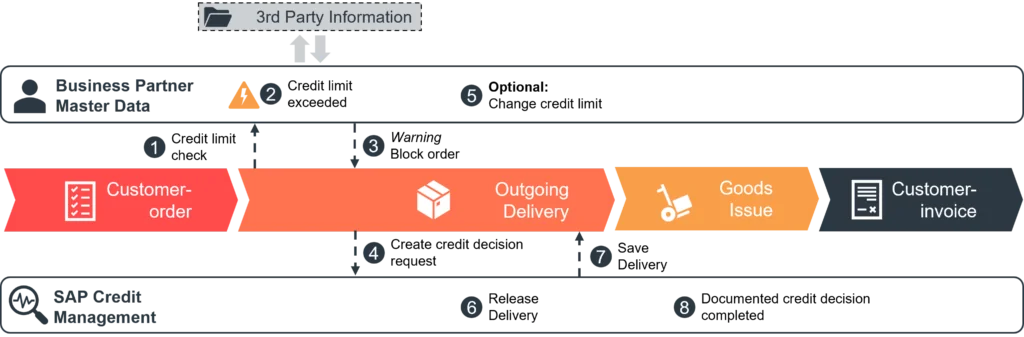
The standard functionalities are essentially retained in both SAP Credit Management versions, but are integrated into the new features such as the business partner concept (see Fig. 1). The solution’s focus is on the FI component which is upgraded with a large number of additional detailed and largely automated credit management features via the licensed extension. The goal is to move all tasks in this area to the SAP system.
In SAP S/4HANA, the business partner data relevant for the credit check are bundled in the business partner’s master record, where they can be maintained manually. For this, the role “UKM000 – SAP Credit Management” must be assigned to the business partner and appropriately populated. The role must also be taken into account for the relevant users in the authorization concept. Transaction FD32 which was available in the in the previous Credit Management for maintaining the credit limit at the debtor level is no longer available.
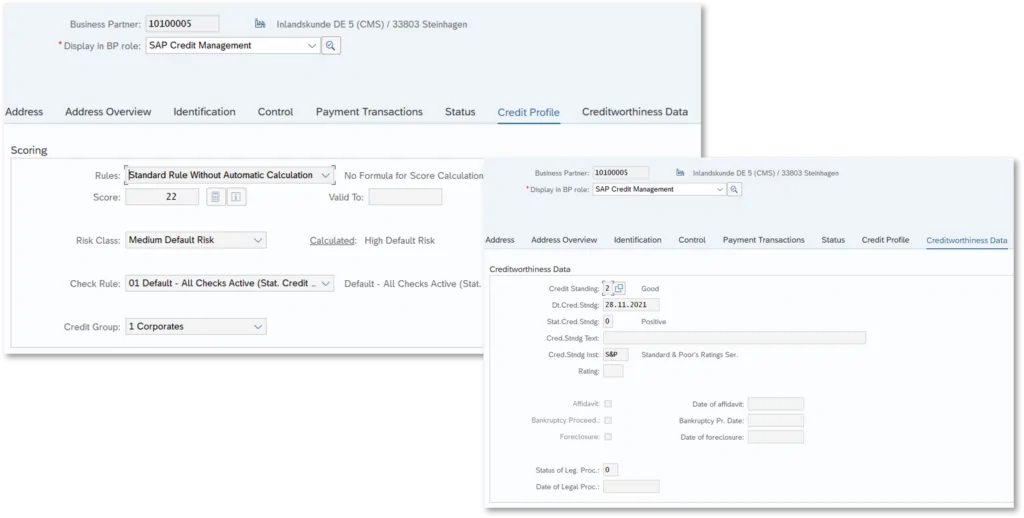
The role UKM000 can essentially be populated via two tabs to maintain the credit profile and credit standing data. This includes in particular the risk class, checking rule, credit group and scoring data. In the credit standing data, it is possible to store information on the last scoring or – for the legal department – events such as initiated insolvency proceedings; these usually originate from official sources such as the Federal Gazette.
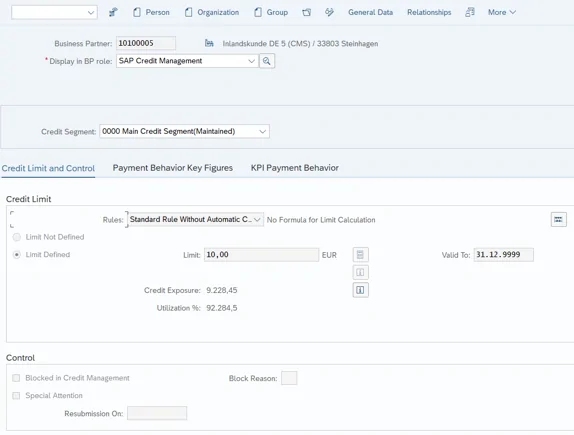
Via the header area, the credit analyst can maintain the credit segment data, such as the credit limit, to be granted based on the credit standing check and risk determination. In the same area, a credit limit check can be simulated and the customer blocked in the Credit Management.
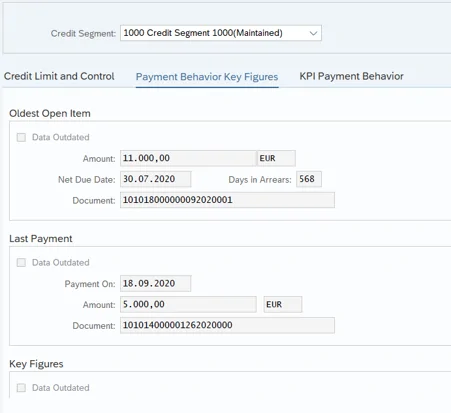
If further information – e.g. relating to payment behavior, the current highest dunning level or the oldest open item – is needed for maintaining the master data, this can be displayed directly in another tab. The key figures can be imported from BI or cloud solutions or, for debtor data, supplemented via the report UKM_TRANSFER_VECTOR (Send key figures on payment behavior).
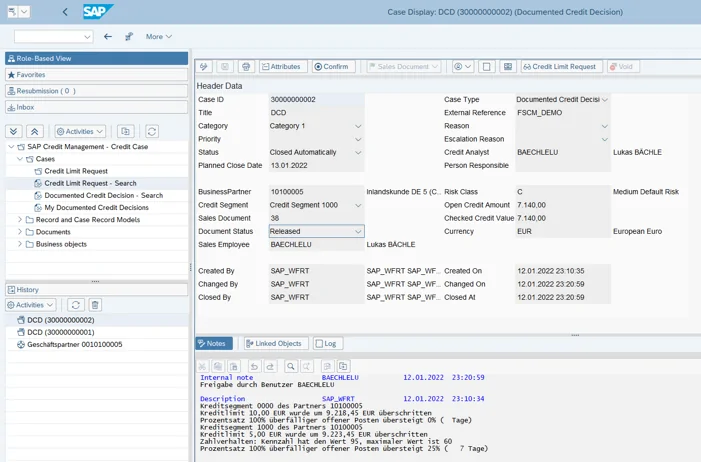
If the credit standing check has a positive outcome and the credit line is to be adjusted, SAP Credit Management initiates a credit limit request. In the case of a negative outcome, the system generates a “Documented Credit Decision” which can be used in the course of the credit management to check whether credit can still be granted. In contrast to the credit limit request, a document or account is blocked in the process. A dual, triple or quadruple control principle can be configured for the initiated workflow. In addition, documents, notes and documents can be attached, providing for plausibility and transparency throughout the credit decision.
The former procedure for blocked orders via transaction VKM1 can continue to be used, but is being replaced successively by the Documented Credit Decision process.
The responsible credit officers can check, approve or reject the Documented Credit Decision via the TCodes SCASE or UKM_MY_DCDS and leave a note. The sales staff access the web-based customer credit information via the “Display Credit Master Data” app (TCode UKM_BP_DISPLAY).
To use the new SAP Credit Management, the component must be enabled in Customizing using the Business Add-In (BAdI) UKM_R3_ACTIVATE. FSCM also requires the configuration of the communication between the system components Sales and Distribution and SAP Credit Management. To do this, BAdI BADI_SD_CM must be enabled.
In contrast to Basic Credit Management, the license-requiring Advanced Credit Management package allows a business partner’s internal creditworthiness to be calculated automatically. For this, the system automatically derives the risk class from the internal creditworthiness and calculates the credit limit using the Credit Rule Engine and the Formula Editor. Users can define their own calculation and derivation logics or import the rating from external third-party agencies. The XML file can be imported manually or via a direct connection. The necessary interface must be developed as part of a project. Alternatively available is the standard SAP Cloud for Credit Integration solution (which also requires a license) into which credit ratings from selected providers are already integrated.
SAP Credit Management can be implemented as part of a greenfield approach or migrated from an existing system to the new environment in the course of a SAP S/4HANA conversion project. Important aspects of the migration are the master data, credit exposures and the initialization of the credit decision. The settings relevant for the conversion can be found in Customizing under the item “Conversion of Accounting to S/4HANA”.
Minimize Credit Risks with SAP Credit Management
You’re interested in implementing SAP Credit Management? We’d be happy to advise you without obligation.
Don't miss a thing.
Subscribe to our latest blog articles.